Using AWS Glue to Accelerate Your AI & Analytics Initiatives
As AI and analytics becomes table stakes for businesses, there is a need to manage and utilize many different sources of data. These data sources can be of many different kinds – structured, semi-structured and unstructured. As I outlined in my blog earlier this year, one of the top challenges faced by data scientists is getting timely, high-quality data at the right time so that they can allocate their time to analysis and insights, versus data management. AWS Glue comes as a savior. At its core, it is a fully managed cloud ETL (extract, transform, and load) service that makes it simple and cost-effective to categorize your data, clean it, enrich it, and move it reliably between various data stores and data streams. But I feel that it can be a powerful tool that can truly help accelerate your strategic data initiatives. In this blog we’ll look at when to use it, and what to think about before implementing it. What is AWS Glue Enterprises often sit on data mines, not fully extracting the monetary benefits of leveraging the insights for operational improvements, customer experience, and revenue growth. On average, almost 70% of a data scientist’s time is spent cleaning incoming data, aggregating the sources, and making them ready to be used for analysis. This is where AWS Glue comes in. It helps you monetize your data debt, and sets up the roadmap for higher overall organizational maturity. AWS Glue positions three core components at the highest level – a data catalog, ETL processing, and scheduling. By considering the architecture in this manner, we logically begin to focus on the outcomes rather than the procedural aspects of data management. We think this is a very nice soft benefit. The AWS Glue Data Catalog is used to track all data, data locations, indexes, run metrics, and schemas. It makes the data accessible, converting unstructured data into preferable schema-oriented table formats. It uses “crawlers” and “classifiers” to assist in the identification of data schema and its creation in the Data Catalog. AWS Glue crawlers can crawl both file-based (e.g., unstructured) and table-based (structured) data store via Java Database Connectivity (JDBC) or native interfaces. It can securely connect to multiple data sources and saves the time by doing away with the need of reconnecting every time. Then together, the three components significantly reduce manual effort by automating the entire data discovery and aggregation process. Consequently, we also reduce the probability of errors. The second major benefit is that AWS Glue is serverless. This means that there is no infrastructure to set up or manage. In turn this implies that the agility factor to go from data to insights is high. Illustrative Case Study On a recent project, the operations team was facing challenges in getting their key customer analytics reports out on time. There was a significant level of manual effort needed for data pipelining (integration) from multiple sources. The data had to undergo several levels of adjustment to be ready for analysis. Inconsistencies between data sources had to be resolved very frequently. This overhead was affecting reporting and business intelligence latencies negatively. As a result, the client team was encountering challenges in their ability to engage their customers in data-driven performance conversations to create the right strategies for the next customer marketing cycle. In order to meet this challenge of streamline business reporting and analytics process, we used Glue to act as a supporting tool to the regular process flow. Multiple files containing millions of records every cycle were processed. Some of the data was structured (e.g., customer data) while some was semi-structured (e.g., advertising information) and the rest of it was unstructured (e.g., user generated content). An important point to note is that we masked the data (using PySpark) that was processed by Glue to maintain compliance and reduce risk. Processing was in memory, data was access restricted, and only masked data was allowed as output. We customized the sorting and filtering in the business reports and other output in a way that no sensitive information was compromised. The data sources were segregated into specific folders. Then the AWS Glue crawlers helped us crawl the files and structure the data properly. Glue split the jobs and ran them in parallel so we could truly leverage the power of the cloud. With the latest Glue updates, we also now get much better UI and faster processing. Since AWS Glue is serverless, we were able to start quicky with a low cost, pay-as-you-go option. One of the key benefits was the trade-off between time and cost. We went from a largely manual process to an automated process which was a huge time saving. Finally, there are inherent benefits of a cloud-based data infrastructure over the traditional approach. We were able to store and process very high volume of data which otherwise would have required a significant scalability management overhead in terms of on-premise infrastructure. What to watch out for? One consideration is that as you adopt any cloud-based solution, costs can quickly rise. One of the ways we were able to contain that is by being conscious of what we needed. For example, for structured input we used limited AWS Glue features such as crawlers that look at the incoming file formats and validated them on an automated schedule. Since we had a lot of files, we also found it very useful to use crawlers to help redesign the files. We also ran a lot of processing outside the Glue environment using Python because the processing within a managed cloud service can quickly get expensive. Finally, like any technology tool, sound knowledge and real-life experience is required in order to maximize the benefits you can get from AWS Glue. Creating a robust data management strategy using a top-down approach using design thinking principles is very helpful. It allows you link the enterprise rollout of AWS Glue in a manner that is substantiated by associated business benefits at every stage. Next Steps We recommend that you give AWS Glue a try. It can help you get started quickly with your data management efforts and ROI can be realized within as little as 6-8 weeks. We can help you run a pilot, and conduct a discovery workshop to create a roadmap that matches your business goals. Take our data strategy assessment to see where you are on your data management maturity.
The Biggest Data Engineering Challenges of 2022
The dynamic data engineering technology space of today is propelled ahead by the decisive shift from on-premise databases and BI tools to modern and advanced cloud-based data platforms built on lakehouse architecture. Today’s challenging data environment stipulates, reliance on multiple technologies to keep up with scale, speed and use cases. The cloud data technology market is advancing swiftly, and includes an extensive set of open source and commercial data technologies, tools, and products, unlike the on-premise data warehouses of the past. Organisations are developing DataOps Frameworks and Functions to be maximize the value of their data and to be in relevance. To enable automated and continuous delivery of data to business intelligence analytics and data powered products, processes and DataOps tools are in place. As per a recent study by Gradient Flow and Immuta, respondents cited these areas as the most challenging in the data engineering space: Data Quality and Validation; Monitoring and Auditing for Compliance; Masking and Anonymization; and Data Discovery. We at Ignitho have been building capabilities, across our Data Engineering Practice to mitigate these challenges in the most holistic way possible. With potential sources of error increasing day by day; factors like volume, variety, velocity, data source type, and the number of data providers, are playing a huge role in how we face the concern of data quality. Solutions based on our Informatica and TensorFlow Data Validation capabilities have helped our clients tackle data quality issues and challenges impacting critical and products, depending on the accuracy of Data. At times, when organizations’ have to handle myriad of data sources and data types, such as unstructured data consisting of text, images, audio, and video; the data integration solutions with Apache Spark, dbt and Hive as well as managed services like AWS Glue, Dataform and Azure Data Factory has been adding value to our clientele’s data compliance efforts. Data Masking and Data Encryption are distinct data privacy solutions. Ignitho’s regulated approach on GDPR, HIPAA, CCPA, and SOC 2 has been pivotal in removing the misconception among data stewards on Data Governance and Data Privacy when considering data anonymization solutions, that encrypted data is indeed a form of data masking. A recent study indicated that close to 1 in every 4 organizations, do not have a structured Data Catalog or Discovery tool. As they grow, the amount of raw and derived data they generate and store rises, and users need tools to help them discover the right data resources. Ignitho’s expertise in the areas of Google Data Catalog, Collibra, and Azure Data Catalog, are assisting organizations drive adoptability. Headquartered in the US, Ignitho services its customers through its offices in London, UK, and New York and Richmond, USA, and its development centers in Brighton, UK and Kochi, India. We are rapidly gaining recognition as a market leader in Frugal Technology Innovation for Enterprises – the ability to do more with less.
Introducing the Frugal approach to Technology Innovation in Enterprises

In the following 3-part blog series, the aim is to impart a basic knowledge of what “frugal innovation” actually stands for and what it means in an enterprises’ context. The next two blogs will talk about the principles that guide frugal innovators and why enterprise CIOs must take a closer look at the possibilities of frugal innovation. “Frugal Innovation” is defined as the art of overcoming harsh constraints and innovating sustainable products with limited resources. As a concept, it is not new and has been around for at least a decade, largely prevailing in the socio-economic context of developing countries like India, Kenya, Brazil, and China, where we have seen examples of frugal innovation by grassroots entrepreneurs to multinationals across sectors. At the grassroots end, examples include clay refrigerators used to store vegetables in rural areas where the lack of electricity is a constraint to baby warmers designed to help premature babies maintain their body temperature and preserve their lives. At the multinational end, pioneers of frugal innovation include the likes of GE, Siemens and Renault-Nissan, who have built low-cost solutions overcoming the constraints of energy and environmental challenges. Frugal Innovation creates value for Individuals, Businesses & Society Frugal Innovation begins with identifying opportunities that arise from adversity. Innovative minds reframe problems and convert them into opportunities. Maximum effort is made to flex available assets and convert them into sustainable solutions appropriate to the problem, the situation and the end user. Frugal innovation, therefore, unleashes the creativity in individuals and helps them to do more and better with less. Frugal innovation is thus also geared towards creating value for individuals, business, and society through the efficient use of available resources. Because of the transformative power of the concept, I have been researching it along with co-authors for over a decade now. In 2012, along with Navi Radjou, an innovation guru and winner of the Thinkers50 Innovation Award, and Simone Ahuja, a film-maker and consultant, I wrote Jugaad Innovation, a bestselling book about frugal innovation in emerging markets and what large Western corporations can learn from their emerging market counterparts. Hailed by the Economist as ‘the most comprehensive book yet to appear on the subject of Frugal Innovation’, the concept of frugal innovation attracted a lot of attention in the West for the West. So, Navi Radjou and I then went on to publish a follow-up book called Frugal Innovation: How to Do More with Less that focused specifically on frugal innovation in developed economies in the 21st century. In the book, we look at large companies such as Unilever, Renault, GE, Siemens, GSK, and others that are using the frugal principles to drive innovation in resource-constraint environments globally. Frugal Technology Innovation for Enterprises Over the last decade or so, we have seen a tremendous explosion of frugal innovation in various socio-economic contexts. Now an interesting question arises: can frugal innovation be applied to bring technology innovation to enterprises? Ignitho has taken the bold, pioneering step of adapting this concept to drive Frugal Technology Innovation for Enterprises. I have been collaborating closely with Joseph Olassa, co-founder and CEO of Ignitho, to actively promote Frugal Technology Innovation for Enterprises in the US and UK markets. Joseph has been a leading advocate of this approach and has presented his ideas at various global conferences. Combining my research on frugal innovation with Joseph’s expertise in technology innovation, Ignitho and I have successfully developed a frugal methodology to rapidly prototype business ideas and scale technology innovation in enterprises facing time and resource constraints. Ignitho’s disruptive new approach can help unlock efficiencies to innovate using available resources (money, time, people), to deliver tangible outcomes for the business using technology. If the concept of Frugal Technology Innovation interests you, stay tuned for my next blog which talks about the principles guiding Frugal Innovators and how they can lead enterprises to achieve successful Technology Innovation.
4 Key Principles For CIO While Selecting An Innovation Partner
Introduction: In today’s complex and fast changing world, the role of the CIO is not an easy one. Balancing the demands of the commercial business, key IT sponsored programmes, compliance (The California Online Privacy Protection Act, The Computer Security Act of 1997 and GDPR to name a few) and let us not even go into the territory of Digital and Agile working practices! It’s not surprising that IT innovation usually ends up low down the priority list. Add this to the challenge of securing funding for efforts that may not have clear paybacks then the result is Technology Innovation is often ignored completely! Is this acceptable? Technology Innovation – Ownership Well the short answer would be everyone and anyone in an enterprise could and should have a role. But where should ownership reside? I set it hard to argue that there is no better place than that of the office of the CIO. The question CIO’s need to ask is ‘am I comfortable’ with that responsibility and maybe ‘am I comfortable’ with it outside IT? If you come to the conclusion that you should own it then you need to take actions to make this happen. Plan In order to really gain momentum, there are a few key principles that need to be considered: The need to allow anybody in an enterprise to put forward ideas – Technology ideas are no longer the exclusive domain of IT. Accept and embrace it. The enterprise innovation groups are bombarded with unlimited ideas coming from various internal teams. The issue is in identifying the right idea and the required time to nurture these ideas. Keep the process light – don’t hide behind monolithic processes (read barriers) – The CIO’s we speak to often say that they mostly qualify ideas based on factors such as exertion, money, production, and achievement. This process is high cost and time-consuming, resulting in ideas being scrapped even before they are properly considered. The key is to identify ideas with minimum effort and filter the ones with maximum potential benefit. This is easier said than done using monolithic processes in innovation. Resources – plan some time to look at ideas to find the best potential innovation idea. While considering an idea CIOs are forced to consider the following factors such as the effort, capital and output required, to turn these ideas to functional products. Budget – allocate some resource/money – In today’s digital era, CIO’s often shy away from adopting a ‘silver bullet’ approach to technology innovation. CIO’s should think of ways of starting small and gain some traction. Be smart – look into the market for ideas – for example have you looked at RPA and how you could use it to improve your business processes (including IT) or extend a legacy system or two. What are businesses in other industries doing? Could you ‘migrate’ the model to your business? Partner – To build a competitive advantage, enterprises need to carefully select their innovation partners. Enterprises should look to select an innovation partner who is able to bring a global delivery model leveraging onsite and offshore advantages to the party. Innovation Partner For those ideas that require software to be built the golden rule is not to spend any more than you must in order to prove or disprove the idea. Look for a partner who does not treat innovation projects the same way as mainstream IT projects – business cases/project and expects the same guarantees on the investment return. Enterprises should look for innovation partners who give preference to ROI-backed innovation or in other terms sustainable innovation. An equally cost-effective method for sustainable innovation is adoption of Frugal Innovation methodology for technology innovation by enterprises. Ignitho Technologies, headquartered in the USA, and with its offices in New York, USA & London, UK, and its innovation labs & development centres in Richmond, USA, Brighton, UK and Kochi, India, specialises in Digital Applications – The ability to start small and deliver quick outcomes which are inherently scalable, for the web, mobile and cloud and Innovation Pods – The ability to build focused agile pods with cross-functional teams delivering faster prototypes and digital solutions. The secret of success for Ignitho lies in their Frugal Innovation methodology – “the ability to do more with less” – developed in collaboration with a world-renowned thought leader from the University of Cambridge. With its Frugal Technology Innovation methodology, Ignitho works with enterprises to identify potential ideas and using the geographically spread innovation labs to build MVPs. This allows enterprises to take up a step-by-step approach to technology innovation instead of going for the big bang approach which could, in turn, hurt their IT budget. In summary, the CIO’s should invest the time and take the lead on Innovation and should not be afraid to do so. There are great tools and partners who can help CIO’s succeed on the journey. You may not find a ‘silver bullet’ idea but if you start the journey with a partner like Ignitho, you will find things that can improve your business and that can’t be a bad thing.
A CIO’s guide to the need for Frugal Technology Innovation in Enterprises
In our previous two blogs in this series, we discussed what Frugal Innovation is, and the five principles that guide Frugal Innovators. While still relatively unknown in an enterprise context, the Frugal approach to Technology Innovation in the Enterprise may just be the golden ticket for CIO’s and business leaders to help escalate the pace on effective innovation at a time of rapid business disruptions caused by COVID-19. CIO’s and business leaders already recognize that innovation is no longer a luxury but a necessity for an enterprise today. Recent corporate history shows that innovation could well be the difference between exponential success or rapid decline in the enterprise. Consider the well-known examples of Kodak and Blockbuster, giants in their time but who no longer exist today out of poor reactions to the changing business environment and consumer behavior. Kodak underestimated the potential of digital photography which later disrupted the entire industry and replaced its film-based photography. Similarly, when Blockbuster CEO John Antioco and his team laughed at the proposal of partnership with Netflix in the year 2000, little did they know what waited for them in the coming years. In an enterprise context, innovation is normally a result of a burning need, an emerging trend or a popular new technology platform, or a convergence of these. For example, look at how the enterprise landscape has changed because of the coupling of a need with a new technology trend, such as gaming, social media and the emergence of super-powerful smartphones and tablets. When mobile took over the user experience factor, businesses had to adapt and deliver mobile-friendly applications to attract and retain their customers. While clearly recognizing the need to innovate quickly, enterprise CIOs face practical challenges in using a one-size-fits-all, big bang approach to all technology innovation. Our discussions with over 100 CIO’s have thrown up the following top issues. Lots of ideas but no sufficient bandwidth to nurture Innovation in an enterprise is often not a problem of finding ideas. In many scenarios, the CIO or innovation group is bombarded with a plethora of ideas coming from various internal sources. The problem therefore really lies in finding the necessary bandwidth to nurture these ideas, to run alongside larger transformation initiatives and business-as-usual. Need help in qualifying ideas and creating business cases The CIO’s we spoke to tell us that they would welcome advice and extended bandwidth to qualify ideas based on factors such as effort, capital, output, and success. Often though, this comes at a high financial cost and may also be time-consuming, resulting in ideas either being dropped or a loss of the window of opportunity. Identifying ideas that require minimum effort and provide maximum output is easier said than done using conventional approaches to innovation. Not enough good ideas that qualify While there may be a long list of potential innovation ideas, sometimes innovators face the issue of good quality ideas. When the success rates of these available ideas are compared with certain metrics such as the effort, capital and output required, many of them fall off the scale, resulting in a lot fewer ideas. Limited budgets can only nurture a few ideas Big bang transformational approaches to innovation are normally very expensive and time-intensive, thereby consuming whatever little budgets were available in the first place. Once again, this may cause other potentially brilliant ideas to fall by the wayside for lack of available budget and resources. No designated budget for innovation in non-core solutions Surprising as it may sound in today’s digital era, CIO’s are still often stifled by the lack of appetite within the enterprise to invest in new ideas. They must work very hard to push an agenda of innovation to run alongside business as usual initiatives. As a result, most ideas fail to get off the ground using the traditional big bang approach to innovation. Frugal Technology Innovation may be the answer Ignitho’s Frugal Technology Innovation methodology (Doing More with Less), built-in conjunction with Jaideep Prabhu, one of the world’s leading authorities and best-selling author on the subject, helps tangibly demonstrate ideas to the business stakeholders using limited resources through Rapid Prototyping, which can be ramped up to Scalable Solutions based on early success. Ignitho’s Innovation Labs, its unique peer ecosystem, and proven high-quality business and technical resources, are already translating business ideas into successful reality for enterprises. Talk to us today to find out more and get started on your own Frugal Technology Innovation journey in your Enterprise.
10 Steps To Consider While Selecting An IT Outsourcing Partner

The current predicament of a CIO while selecting an IT outsourcing partner Today CIO’s have an added responsibility to transform businesses into a better enterprise. The new age decision makers, drive their business through dynamic markets, delivering on an architecture that is built on a scalable platform and which has the capability of rapid response and providing tools that offer insight and decision support. According to a study conducted by a top analyst firm, 31% of IT services have been outsourced in 2017 and this will continue to grow in future. Outsourcing has revolutionised the way business is done in almost all sectors. Though a gradual process which evolves with time and as per the latest requirements of the industry, the basis of outsourcing business is to accelerate the pace of one’s business and increase its efficiency. Outsourcing is certainly a blessing for the business community in today’s dynamic market. But the process, or steps in selecting “the right IT outsourcing partner,” need to be performed after careful analysis of many factors, any one of which, if overlooked, can put an outsourced project, in going way over the projected timeline and budget and leave the business or the product way behind their competitors in its go-to-market. Factors often associated with outsourcing, such as over-promising, under-staffing, security breaches, culture shock, and many other factors can turn profit margins into cost overruns and software that falls far short of the client expectations. To build a competitive advantage enterprises need to carefully select an IT outsourcing partner. In this blog, I will discuss some of the steps you need to consider before selecting an outsourcing partner for the purpose of structuring a global delivery model leveraging onsite and offshore advantages. 10 steps to consider while selecting an IT outsourcing partner 1. Identify the need for Outsourcing First and foremost, identify your need to outsource. Many enterprises outsource as part of cost reduction. Up until a few years ago cost reduction was the major reason to outsource. However, it should no longer be looked at as the sole driving force. You should be looking at current and future staffing models how you can improve inefficient processes what non-core activities you don’t need to do yourselves as drivers, and, what financial benefits you can achieve You should think long and hard about the benefits that can be gained from having a distributed and flexible staffing model to cope with the inevitable ups and downs in the dynamic market. 2. Support from the Board It is inevitable that some members of your staff will not be in favour of outsourcing. Some of their concerns may be purely self-preservation but others may be genuine perfectly valid issues and it is vital that all are listened to and that the senior team speak with one voice in detailing the reasons for outsourcing and benefits it will bring. The board need to see and understand the benefits and champion the relationship between the non-IT fields and outsourcing. Therefore, to be successful there must be buy-in at the most senior levels within the company, especially the HR as the word redundancy might pile up and make it harder for the outsourcing companies. 3. Identify an IT partner with the same rigour and passion of the larger corporates If you’re one of the Fortune 500 firms, outsourcing vendor size may not be an important factor, but for smaller firms, getting the attention of one of these large corporates can be tough. While selecting an IT partner, verify the expertise of the core team’s background. For example, Ignitho’s co-founders having previously led business units for the likes of Accenture, Mindtree, Cognizant and HP, as well as other senior professionals who have joined Ignitho from the likes of Capgemini and Infosys, enables us to deliver for our customers with the same programme rigour and approach to top quality, without the engagement overheads of bigger industry players. 4. Cultural fit of the IT Partner As responsible IT executives before selecting your partner, you will have performed due diligence, take up references, go on site visits etc. However, you also need to consider the cultural fit and the size of organisation you are partnering up with. You don’t want to be a very little insignificant player; the retention of whose business is neither here nor there to the outsourcer. Similarly, you need a partner that can meet the needs of your organisation with very little or preferably no delay at all. Think about your partner as being a long-term strategic fit and not a short-term tactical fix. For example, Ignitho’s global Sales & Delivery presence provides you, local touch-points at every stage to facilitate a smooth transition and ensure any cultural differences are dealt with quickly and seamlessly. And a unique and strong CIO Ecosystem provides you with peer guidance from locally based ex-CIO’s to “get it right the first time.” 5. Check for expertise in multiple software technologies The expertise in multiple software technologies is often overlooked but is crucial to the success of any outsourcing deal. Choosing a vendor who knows only a few technologies, even if they’re best in class in the ones you think are right, risks the “hammer and nail” problem: to those armed only with a hammer, every problem looks like a nail. Remember, you’re hiring the outsourcing vendor for expertise you don’t have internally, so be careful not to reproduce your own limitations in this choice. Look for a partner with developers in a wide variety of technologies to increase your chances of success. At Ignitho, our delivery strength lies in the robust pool of experienced, technically competent resources across Microsoft, Open Source, Java, Mobile, Machine Learning and Augmented and Virtual Reality technologies. 6. A Clarity in the Requirements and What is Actually Being Outsourced Make sure left and right hands within your team know what is being proposed. You don’t want manager A thinking you are outsourcing Networks and manager B thinking you are outsourcing Storage. Similarly, you need
A Guide to Innovation Pods: The Future of Enterprise Delivery Model
As a C suite executive your business growth has never been by mere chance; it is the result of the right strategies and catalysts working together for your success. In this journey of building a mighty business for your company one of the tricky challenges that you might have faced is to be versatile in a dynamic and massive business environment. The questions are many as to how to rapidly adapt and develop ideas to align with the changes, capitalizing and navigating around the opportunities and risks efficiently or how to integrate the agility that you see around within your company. The answer lies in how you distribute the control to make the decisions regarding a project promptly with close alignment with the clients. This could only be achieved through autonomous entities that can act on their own without interfering in other business activities that exist within your work ecosystem. Innovation pods An innovation pod is a small, autonomous unit that is cross-functional enabled to deliver projects that the clients appreciate through distributed agile methodology. With the digital switch-over that’s occurring at a fast pace across the domain, emerging innovation pods that convene multi-functional teams, bringing together design with technology in a project to get the best out of the idea, has taken hold as the brand-new centers of excellence (CoE) that will transfer the optimal value in these critical times. Innovation pods are employed to have a seamless delivery process, focusing clearly on the outputs and outcomes that you deliver to the clients. Pods are independent and scalable One big-time advantage of the pods is they are autonomous units that are functioning ahead of the “ripple effect” that might affect the usual operations within the company. They are free to innovate and endorse new work patterns and workflows; devoid of permissions. These pod-level innovations could be well adapted into multiple pods as this process is rather frictionless and productive. As pods are modular, adaptability becomes much easier which makes it more scalable and competent. There exists a good deal of latent skills within each pod that enables you to scale up when the need comes- focusing on the client’s requirements. When the time or the demand comes this digital pod can be reproduced into multiple pods bringing in new members who are cross-functional, thus minimizing the growing pains. Innovation Pods and Agile Methodologies Agile methodologies are gaining momentum since it has created a mindset that has moved far beyond a mere software development team. Today, leaders in the digital domain are employing agile methodology to transform their business workflows and culture. It is with this agile methodology that the concept of digital pods become more prominent concerning the way they ideate and function. An innovation pod is assigned throughout to a particular project; recurrent and consistent in its structure at the same time. Each pod will be having its unique sprint schedules to focus on. Consistency is one of the key aspects that is behind a productive creation and management of agile pods. Significant roles such as scrum masters are expected to be kept constant throughout the project along with other key responsibilities. Right from developing the hypothesis to maintaining and scaling the Minimum Viable Product (MVP) the pods are required to maintain steadiness. The innovation pod’s engagement model comes hand in hand with the agile methodology that has the following steps in common. Scoping– The project is scoped out thoroughly crisscrossing the client’s requirements. Kick-off– Initiate the project after sectioning off the project into phases. Discovery– From the several, critical problems that the client is facing are prioritized for the ease of building. Framing– Through funnel methodology, the solutions are generated for the problems based on their significance and urgency. Define– The solutions are defined for their integration into MVPs. MVP– A Minimum Viable Product (MVP) is developed incorporating the specified solutions. Iterative delivery– After the first phase of the cycle, the product is delivered which then kick start the second phase of the project. To maintain consistency, the pods are expected to be the same throughout the delivery process right from the scoping estimation to the iterative delivery. This is to make sure that the functional capability, scope of the work and the creep along with customer satisfaction remains intact in every step that the pod takes in the project. In this process, stakeholders on both sides become “Co-Innovators” where the enterprises are encouraged to make critical decisions during the early stages, thereby reducing risk in large scale investments. Align the pods to your agile methodology In order to maintain the spirit of the agile methodology, your innovation pods must be aligned in such a way as there exists a cascading effect happening right from the methodology to the pod members. To achieve this there are certain basic functions that your enterprise has to follow on: • Kick start the transition to agile pods by training the pod members in the right direction throughout the onboarding process. • While you generate the teams for the pod, take into consideration their skillsets and how they complement each other. • Provide the right autonomous control within the pods to make innovative and progressive decisions. • The scrum master should be sharing the best practices to be followed after the right ideation within the team and should encourage an open learning environment. • Make the right use of the pods’ skills as much as possible when it comes to the cross-functionality within the structure. • Leverage the use of right stacks and the right technologies as per the client’s requirements. But make sure that the new technologies are not employed in the midway of a delivery process. • Autonomy within the pods is a concept that needs to be ingrained within the pods over time. So be prepared to give the required time to the team to scale up themselves to play their respective roles in full efficiency during the process. Innovation pods can be stated as the future
Role of Innovation Consultant in Industry 4.0
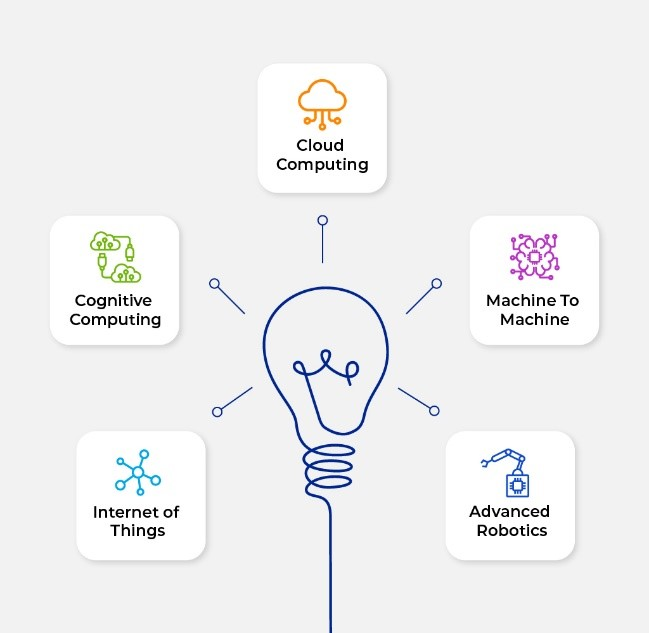
Who is an Innovation Consultant? The multifaceted consulting industry ranging from strategy consulting to social media consulting consists of stalwarts who excavate every part of a business. These consultants identify areas of concerns for businesses, minimize these areas of weakness and strategize how to bring in the maximum output from the areas of strength. Innovation as a term had started gathering widespread usage only by the start of twentieth century and is now part of each industry. Every company is implementing innovation led practices in their growth strategies as well. An Innovation Consultant is one of the more recent roles which the consulting industry has developed because of the disruptions innovation is creating for multiple sectors and industries. Historically, Innovation, for the big players, has always been treated like a top secret lab that was protected from everyone except the researchers in their lab coats. But the fast pace of business and the ever-changing consumer demands have forced these companies to strategize on innovation to stay ahead of the curve or be quickly replaced by the competition. For example, Blockbuster being replaced by Netflix regarding the entertainment industry. Or how companies like Apple, Tesla, and Amazon are pushing their boundaries to meet their customer expectations. Companies like Nokia, Philips and General Electric have faltered with innovation despite having a focused innovation strategy. Innovation Consulting and Industry 4.0 The industrial revolutions that mapped the progress of human kind are a combination of some of the momentous events in history. Starting from the commercial steam engine during Industry 1.0, moving to harnessing electricity in 2.0 and finally ending up with the computers in 3.0. With the advent of interconnected technologies taking over our daily lives, we are already witnessing Industry 4.0. This rapid pace of digitization and innovation in enterprises is signaling towards the rapid adoption of these interconnected technologies eyeing rapid transformation. To keep up the pace with the rapid adoption of these interconnected technologies, the old methods of R&D labs and siloed approaches in innovation is going to hurt these enterprises. In the current scenario, for a majority of companies, innovation is considered a painstakingly long process and if an innovative product or service emerge from these innovation pods, most of them fail. Faced with adversities like lack of productivity, along with increased competition and shrinking innovation lifecycles, enterprises should no longer exclusively rely on internal R&D labs. According to a recent survey conducted by IBM and BCG, enterprises have placed internal R&D eighth out of nine, far behind the general employee population, business partners and customers in terms of important sources of innovation. These adversities and dissatisfactions point towards a tremendous opportunity for enterprises to use innovation consultants as the pivotal point for a new, more focused and rapid innovation process. An innovation consultant who could effectively communicate, collaborate and share information to effectively meet the innovation needs for the enterprises, could make the difference. What should one look in an Innovation Consultant? When one decides to onboard an Innovation Consultant (it can be a person or an organization), there are some key factors that should be considered. Revisit entrepreneurial spirit – Enterprises should identify Innovation Consultants who could help them revisit their entrepreneur self. These Innovation Consultants should help the enterprises to regain the unique value and differentiation these companies theoretically possessed when they started. This would enable these enterprises to sustain their growth while constantly innovating for their customers Create a vision for customers – In order to stay ahead of their competition, enterprises should work alongside the Innovation Consultants and create a roadmap for the services and products being offered to customers. The plan is to achieve these goals before the competition does. Identify and nurture ideas – The Innovation Consultant, along with the enterprises (specifically the Chief Innovation Officer (CIO) or Innovation Lead), should work to identify and qualify relevant ideas based on the effort and capital required for the Return on Innovation (ROI). Apart from the key factors which are mentioned above, enterprises need to analyze some of the key points when approaching an Innovation Consultant. This next section touches upon some of those factors. What should be the approach in innovation consulting? Innovation for enterprises is not just adopting best practices and cost-effective methods, there is also a mindset change which is required from the entire organization if they are to successfully implement an effective innovation strategy through a consultant. Below mentions some of the points: Keep the innovative edge : A common trend among enterprises who start out as innovative organizations is that they lose their innovative edge when they move from a startup to a scaleup. These companies lose focus of their vision as more and more effort go into keeping business as usual. Innovation Consultants can help enterprises to align their organization goals around innovation to retain their innovative edge. A supportive culture : An enterprise without ample encouragement in innovation initiatives is a recipe for disaster as far as innovation is concerned. An organization that gives importance to more conventional methods of Business as Usual would most probably have an adverse environment for innovation. An innovation consultant would provide an outsider view and could suggest improvements to nurture an innovative culture. Ideas : Enterprises are often bombarded with a plethora of ideas. Many times, the problem comes in while filtering these ideas and finding enough time to nurture these ideas. Innovation Consultants can help these enterprises to better communicate and collaborate on the best ideas. Market Intelligence : To stay relevant among the competition, an enterprise who finds it hard to implement innovation might try to become the sheep and follow the herd. Instead these enterprises should work with Innovation Consultants to gather market intelligence to narrow down on decisions based on relevant data. Conclusion Finding the right Innovation Consultant, at the right time, can be very crucial for companies looking to maintain that innovation edge. When working with a person/company to help with your innovation, it is best to partner with a company who lives, eats
Return On Innovation: What You Need To Know As An Innovation Leader
It has been a while that we have been hearing the term “Innovation” almost everywhere and we have been lured to believe in its existential importance. But how many of us have taken a moment to pause and think what exactly Innovation does to one’s business? CIO Magazine rightly points out the insights of Colliers International CIO Mihai Strusievici who had been dealing with the pressure of developing fast and efficient business solutions quickly. He says, “We can create applications very fast, but our business partners may have expectations that if you do it fast, that you also got it right on the first attempt, iteration is harder to accept than one would believe.” This has made the global real estate services team face many challenges as innovation was taken from theory into practice. The biggest worry for Strusievici is the realization that most of the business heads have become frustrated with what they perceive as half-cooked ideas. “I don’t know if the [internal conflict] will emerge as creative energy, or if it will bring [innovation] to its knees out of fatigue.” This is not just the case of Strusievici. There are many Strusievicis out there who face similar challenges when they measure the new ROI – Return on Innovation. Innovation for your Enterprise For many, Innovation isn’t just a representation of novel devices, ideas or methods but the process of revealing a new way of doing things. It can also relate to transforming enterprise models and conforming the changes to attain optimized products and services. To sum up, innovation is nothing but a consolidation of creativity and work which makes a process that utilizes the creative ability. In the enterprise ecosystem, CIOs are in search of business solutions that are novel, inexpensive and caters to their business needs and values. Therefore, for an innovation to thrive, it must be reproduced without being too expensive when solving the specific need. Businesses who vigorously take up the innovation as an opportunity in a highly dynamic business environment are more likely to not only survive but also flourish adequately in the middle of harsh economic conditions. They employ innovation as a technical and strategic tool to build an agile culture to initiate improved business processes. IDC foresees that by 2022, around 80% of the business revenue growth will depend on the digital offerings and operations. This reinforces the notion that there is very little room when it comes to project failure or an obvious tolerance for the quick and simple. Scaling Innovation Challenges Getting Innovation to scale up correctly from an idea to its phased implementation is extremely difficult for even the experts within the business ecosystem. KPMG report on Benchmarking Innovation 2019 states that 60% of the executives who are responsible for Innovation and strategies have cited competing priorities as one of the biggest challenges in scaling Innovation where 59% stated that company culture was another key challenge. Catching up with advances in technology, Innovation leaders are developing their business with IoT, AI & ML, Data Science, cloud computing and via social media. The scaleups in Innovation have been also changing the very basis of the competition that companies had. The increasing accessibility, and availability of innovative business solutions had made a hunger for the enterprises to become Innovative leaders in their fields. Innovation doesn’t have to be something humungous like the next IBM or Microsoft. An excerpt from a CIO Magazine article called What Really Makes Something Innovative? reads, “Sometimes it’s those quiet achievers who can make just as big an impact without having to be ostentatious about it.” It’s just that you must be original in your concepts – pro-active, self-assured and confident to take the risks and get it done quietly. “The problems that I’ve seen with innovation is, we look for ROI in every single project that we try to innovate. You need to have a venture capitalist mindset, especially when it comes to innovation. The company needs to say, ‘I need to invest in 10 ideas, and even if two of those succeed, it can benefit the company.’” says Satya Jayadev, Vice President and CIO at Skyworks. He has set three non-financial metrics to measure return on innovation: the number of Innovation projects it brought to the table, the number of projects amongst them that really got into a Proof of Concept (PoC) and the number of PoCs that went to actual production stage. In FY2019, thus out of all innovative ideas that were brought to the table, 60 got into PoC and 40 got converted into production. He says these metrics clearly indicate the value of innovation across the business. Ideas to ponder for Scaling up Innovation For a business to have an edge in quick-penetration and better connectivity of the markets, Innovation has proved to be vital with its ability to lead them to bigger opportunities. 1. Constantly verify and publicize success The innovators who successfully bring out Innovation take an idea or a hypothesis and scale it up through small executable steps. Throughout the process they constantly verify and publicize their success to their stakeholders. 2. Test cheaper and faster An effective way for Innovation teams to get on the right track is by developing the efficiency to experiment quickly in a cost-effective manner to generate reliable learnings than others in the same domain. The KPMG study has stated the ability to test, learn and iterate as some of the key enablers of success. 3. It’s OK to drop an idea It’s always better to drop an idea that might drain you. According to KPMG, giving too many attempts can result in having insignificant impacts on projects. Because for innovators, failures are steppingstones to success. KPMG survey states that even though organizations push themselves to be more tolerant to failures, it’s not something that they are going to embrace forever. The enablers of return on innovation will always be the right support from industry thought leaders, the right strategy for the innovation initiatives and a team with the optimized